[D]electable coffee may be Dominican Republic’s best kept secret. What is it that makes this coffee so unique? Why don’t we have better access to it?
Farmer-to-Farmer, a program of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), sends volunteers from the United States to transfer knowledge and expertise to farmer groups in developing and transitional countries. As part of my work for USAID, with Texas A&M’s Center for Coffee Research and Education, I traveled to Dominican Republic for two weeks in January to assess and improve resource management to mitigate the impacts of global climate change on the country’s coffee production.
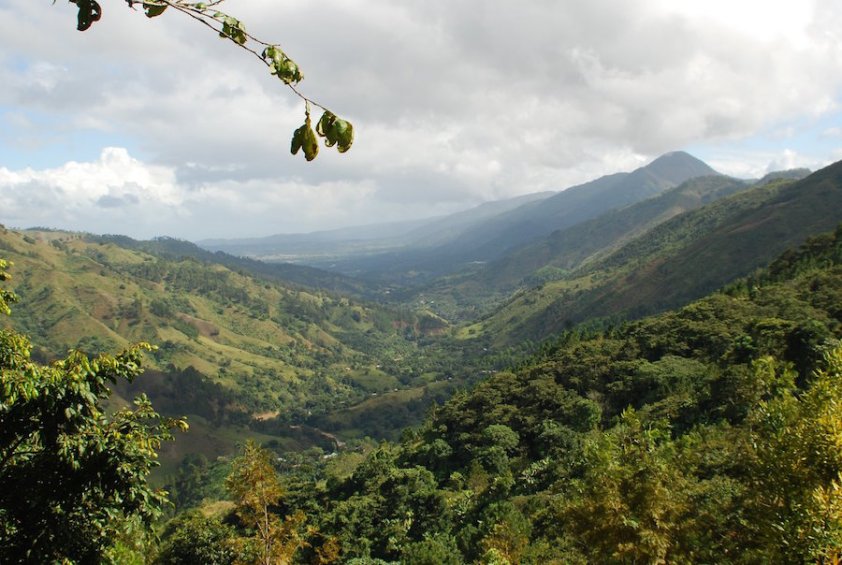
Dominican Republic is known for its pristine beaches and rich history—the country served as Christopher Columbus’s landing place in the Americas, and is birthplace to baseball great Sammy Sosa. What the common tourist may not realize is the Dominican Republic grows some of the highest quality coffee in the Caribbean. Part of what makes Dominican coffee so unique is the absence of a defined rainy season present in many coffee-growing regions.
Normally, year-round rains contribute to the slow ripening of cherries, thus forming a denser, higher-quality coffee bean. However, recent changes in weather patterns have begun to shift this characteristic of the Dominican climate. Although average rainfall has stayed consistent, the rain comes at a higher intensity for shorter time periods. This has exacerbated soil erosion from the steep slopes in the mountains and resulted in the contamination of watersheds. As a result, many farmers have turned to crops other than coffee. However, those who’ve weathered the challenges of changing climate are producing some of the best coffee around.
Though coffee was introduced to Dominican Republic in 1735, the country’s coffee farms are small—usually less than eight acres—and spread across six growing regions. Dominicans almost exclusively grow Coffea arabica, usually typica and caturra varieties. However, these are highly susceptible to Hemileia vastatrix, more commonly known as la roya, or coffee leaf rust, a fungal disease responsible for major coffee crop failures across Central America and the Caribbean. It has become a priority to develop and introduce varieties more resilient to disease and climate change (my research at Texas A&M and the newly emerging Center for Coffee Research and Education, focuses on this development).
Many farms are struggling due to la roya and very old trees, sometimes up to fifty years old. However, something helping many Dominican farmers rebound from this disease epidemic is a focus on diversified farms. Most cultivate coffee under a mixture of shade trees which is important for producing soil cover, slowing water runoff, fostering biodiversity, and creating multiple streams of income.

Coffee production isn’t the only area with room for growth—the economics of coffee in Dominican Republic are changing, too. About 90 percent of the coffee consumed in the country is imported from surrounding countries in Latin America; the highest quality coffee grown in Dominican Republic is exported for sale to European markets. The high domestic coffee consumption in-country means great potential for Dominican Republic to sell their coffee exclusively within their borders until they have increased production to start exporting surplus.
Because of the high rate of importing and exporting, the current commodity chain’s carbon footprint is much higher than necessary. Therefore, identifying opportunities to roast and serve locally is of utmost importance.
Edouard Beauchemin and Coral de Camps of Gente de la Isla are doing just that. They are the first local Dominican roasters to process specialty coffee. Edouard and Coral sell to local grocery stores and coffee shops with the motivation to open their own shop this coming year in Santo Domingo. They are spearheading the specialty roasting market in Dominican Republic using the highest quality coffee and buying organic beans when available. (Gente de la Isla coffee is now available online.)
As more coffee is retained by local roasters and efforts continue to provide better resources for farmers, Dominican Republic has much to offer to the coffee lovers around the world.
—Lauren Fedenia is a PhD candidate in the Department of Horticultural Sciences at Texas A&M University.