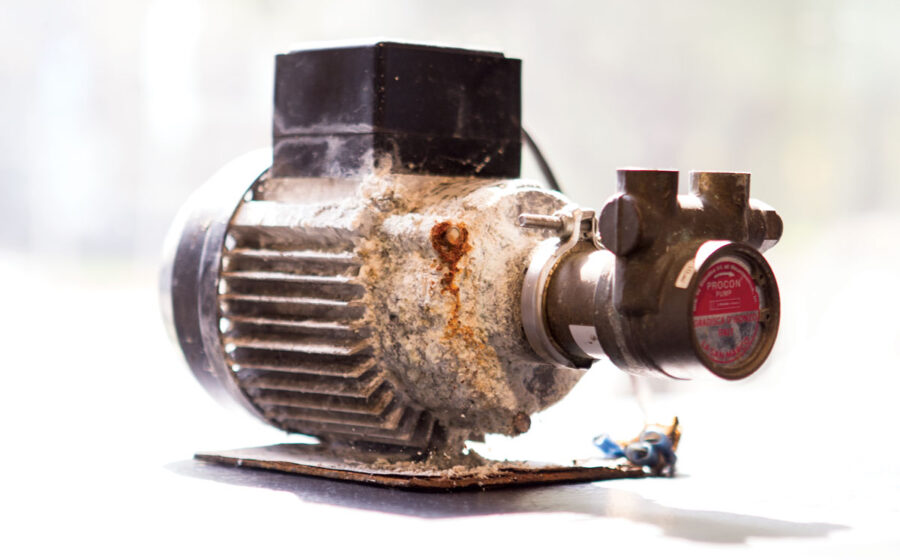
Every veteran barista has a scale-related horror story. It can be as simple as a clogged group head or as expensive as a destroyed heating element.
Unless you actively prevent it, scale is accumulating in your café right now.
Simply put, scale refers to the mineral deposits that amass when water with calcium and magnesium is heated. Ted R. Lingle writes in The Coffee Brewing Handbook, “These deposits occur as the water is heated and the calcium and magnesium make water combine with silica, sulfate, and carbonate to precipitate out of the solution and attach to metallic surfaces.”
As these minerals accumulate, they interfere with proper machine function by blocking valves and interfering with heat transfer. Because scale build-up does not affect the taste of the water, it often goes unchecked until substantial damage is done.
The Makeup of Water
Pure water is, of course, made up of two hydrogen molecules bonded with one oxygen molecule. While using pure water would eliminate scale, it is neither available in quantities necessary to run a café nor desirable for coffee flavor. The exact amount is debated, but some mineral content is needed to aid proper extraction during the brewing process.
“There is a sweet spot where coffee flavor is maximized, and equipment integrity is maintained,” says Maxwell Colonna-Dashwood, three-time UK Barista Champion and co-author of Water for Coffee. The forthcoming book is based on extensive scientific research Colonna-Dashwood carried out with co-author Christopher H. Hendon, a computational chemist who works as a post-doctoral scholar at MIT.
Colonna-Dashwood met Hendon while Hendon was completing his doctoral studies at the University of Bath, where Colonna-Dashwood co-owns two cafés. The two bonded over their mutual interest in each other’s field. “Our goal was to improve our understanding of the water we are working with,” says Colonna-Dashwood, “and how that differs from place to place.”
Water hardness is usually calculated by adding the calcium and magnesium content, but Colonna-Dashwood and Hendon discovered that sum is insufficient. The two minerals behave differently during brewing and should be analyzed separately. “Our book presents a chart that pairs these two components against each other, charting the likely impact on flavor, as we have more or less of each in the brewing water,” says Colonna-Dashwood.
Adjust To Your Local Water
Although Water for Coffee shares an “ideal brewing window,” the best filtration system for a specific coffee shop depends mainly on the local water. “Filtration methods can be broken into two main categories at the moment—reverse osmosis and ion-exchange cartridge,” says Colonna-Dashwood. “They work in specific and different ways. In effect, the source water dictates the type of water that comes out of the other end.”
Colonna-Dashwood’s café, Colonna & Smalls, uses an ion-exchange cartridge, but the water in Bath is relatively soft. More extreme circumstances might require a reverse osmosis system. Whichever system is in place, regular maintenance is needed to ensure it is functioning correctly.
“The problem is that if cartridges aren’t changed regularly enough or reverse osmosis managed properly, then scale problems can hit you out of nowhere in a hard water area,” Colonna-Dashwood says. “The benefit of a soft water area is that scale should almost never be a problem, but getting the best out of the coffee may be tricky.” Colonna-Dashwood recommends using a titration kit to test the quality of one’s water. In the States, café owners and baristas can learn more about their local water supply from water.usgs.gov.
If your café has previously had insufficient water filtration, it will probably be necessary to descale your espresso machine. The most effective way is to disassemble the machine and remove the scale manually, either with a flat head screwdriver or a similar tool.
In some circumstances, it might be necessary to use a citric acid-based descaling solution. One should be cautious about using a cleaner anywhere residue could harm coffee flavor, such as in a water boiler. You also must check your warranty because accessing some components of the machine could void it. In that case, call a professional technician.
The far easier option is to start with proper water filtration. “Ideal brewing water will produce little scale but still has scale potential,” says Colonna-Dashwood. “Over time and heavy use, equipment may need descaling, but if water is carefully controlled, we are talking every seven-ish years or more in a high-volume café.” In other words, do yourself a favor and make sure your water is on point.
Photos by Cory Eldridge
Michael Butterworth is the cofounder of etkincoffee.com and thecoffeecompass.com. He lives in Istanbul, Turkey.
This article was originally published on September 22, 2015 and has been updated to meet Fresh Cup’s current editorial standards.